The Crucial Role of Encoders in Industrial Robot Tool Center Point Precision
The essential traits of industrial robots include speed, power, and resilience. These robots are commonly employed in tasks like welding and lifting heavy components for vehicle assembly. Despite advanced calibration techniques, the positional accuracy of industrial robots has been insufficient for specific operations. This is undergoing a transformation, partially attributed to the highly precise output-side encoders manufactured by HEIDENHAIN and AMO.
The primary catalyst for this advancement has been the aerospace industry, which necessitates highly precise machining operations on exceptionally large components. While machine tools could readily achieve the necessary level of accuracy, they are either too rigid or too costly to be deployed as specialized machines in the challenging job sites and working spaces involved. Conversely, a robot can effortlessly reach any position on a very large component, such as the fuselage of an aircraft, and execute tasks such as drilling and milling.

1. Accuracy is impaired by many factors
However, for these types of applications, it's crucial for the tool center point (i.e., the tool at the end of the robot’s arm) to be positioned and guided with precise accuracy. This requirement poses a challenge for classic industrial robots, as deviations arise from various factors:
-
To attain the necessary maneuverability, robots with serial kinematics, such as articulated robots with six axes, are essential.
-
Each of these axes is powered by a servo motor with a gear train, where zero position error, backlash, and joint elasticities contribute to inaccuracy.
-
The rigidity of the robot’s mechanics is affected by applied forces and dynamic effects during the machining process, leading to negative influences on the absolute position accuracy.
Advanced calibration methods already enable the repetitive movement of a tool center point to a specific position with an accuracy of several hundredths of a millimeter. Articulated robots can achieve repeatability as per ISO 9283 of ±0.1 mm or better, depending on the manufacturer. However, in comparison to repeatability, the absolute position accuracy within the robot’s coordinate system is ten times worse. Presently, articulated robots achieve an absolute position accuracy of ±1 mm, based on their design, maximum range, and maximum load capacity, which is insufficient for meeting the accuracy requirements of industries like aerospace.
In response to this challenge, robot manufacturers have been taking steps to address this discrepancy.
1.1 Step 1: highly dynamic motor control
Traditional rotary encoders are still utilized to provide feedback for the servo motors at the robot’s axes. Given the high control dynamics required by servo motors, robust inductive rotary encoders from HEIDENHAIN, such as those belonging to the ECI 1100 and 1300 series, or multiturn models of the EQI 1100 and 1300 series, are well-suited for this application. These encoders offer high control quality, system accuracy, and resistance to strong vibrations. Their purely serial EnDat interface ensures that even applications exposed to strong electromagnetic interference do not compromise data transfer quality or safety.
These inductive rotary encoders are compliant with safety integrity level SIL 2, category 3 PL d, and with additional measures on the control, they can even achieve SIL 3 or category 4 PL e. Furthermore, these encoders provide the added safety benefit of mechanical fault exclusion against the loosening of the shaft and stator connection. Equipped with this safety feature, these inductive rotary encoders can also be deployed in systems intended for human-robot collaboration.

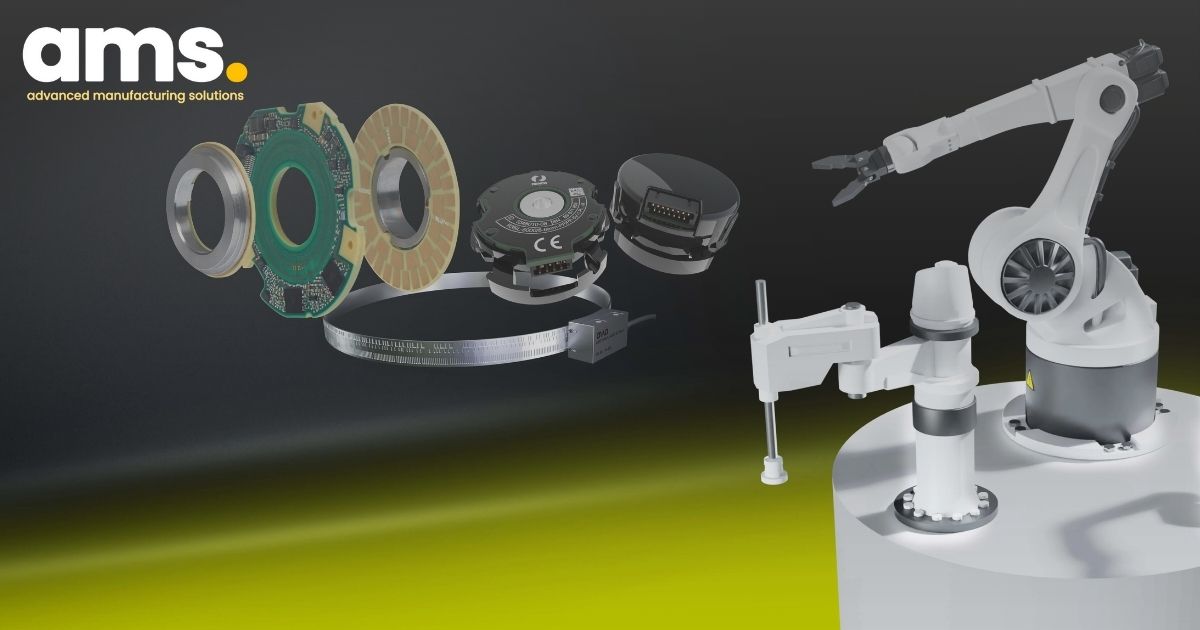
1.2 Step 2: secondary encoders for highly accurate position measurement
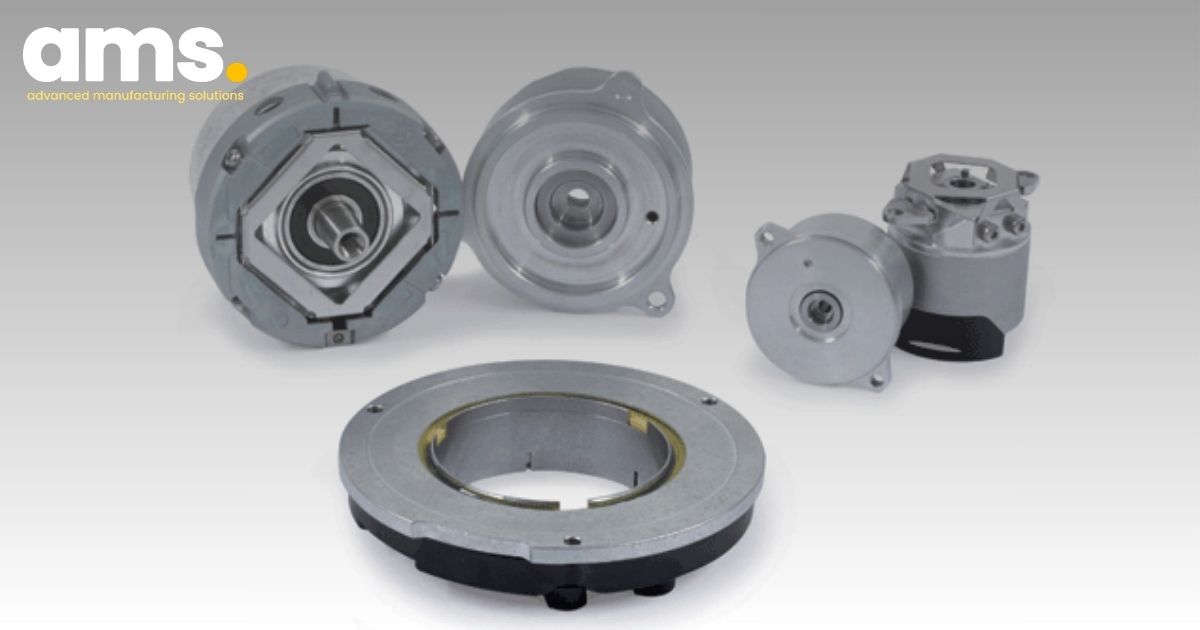
Robotics manufacturers can significantly enhance the absolute position accuracy of their robots by incorporating additional high-precision angle encoders or rotary encoders at each robot axis. Known as secondary encoders, these devices, installed after each gear train, capture the precise position of every robot joint. This setup allows the encoders to counter zero position error and backlash, while also measuring the retroactive forces on each axis arising from the machining task. This comprehensive approach results in a 70 to 80 percent enhancement of the absolute position accuracy at the tool center point.
Modular angle encoders such as the HEIDENHAIN ECA 4000 with optical scanning, the HEIDENHAIN ECI 4000 rotary encoder with inductive scanning, and the AMO WMR angle encoder are well-suited for these applications. Their modular design, featuring a scale drum or scale tape and a separate scanning unit, makes these encoders suitable for large hollow-shaft diameters and the challenging installation requirements often faced in robot systems due to space restrictions. The signal quality of these secondary encoders surpasses that of the rotary encoders on the servo motor, resulting in significantly more accurate position values, even during highly dynamic movements.
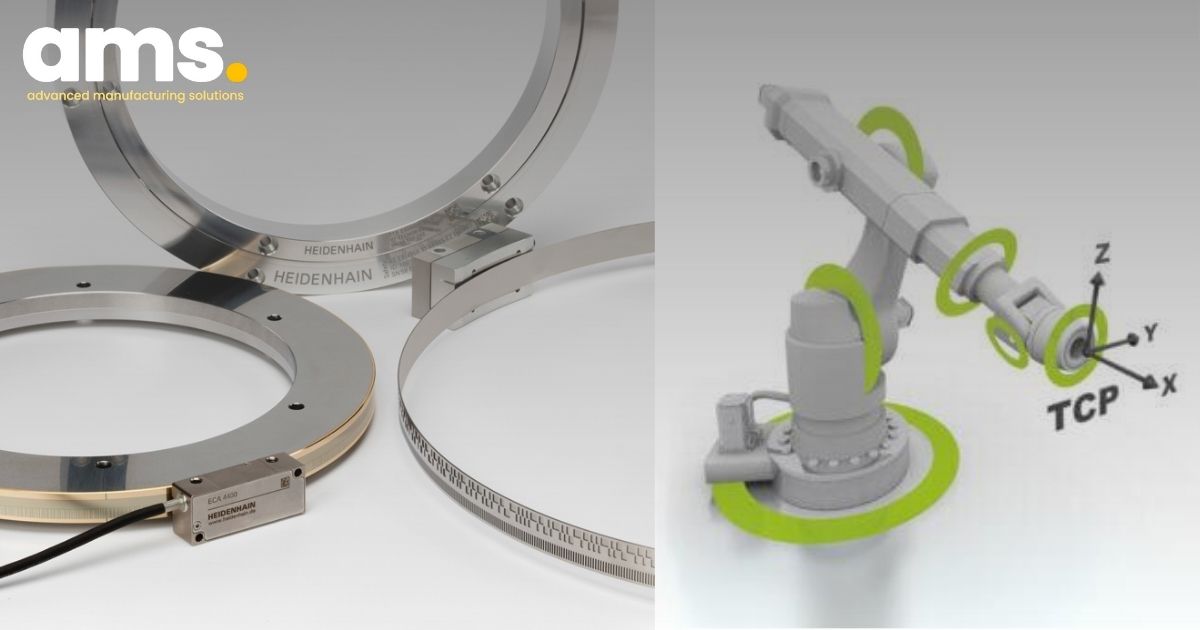
1.3 Step 3: accurate position measurement for movable robots
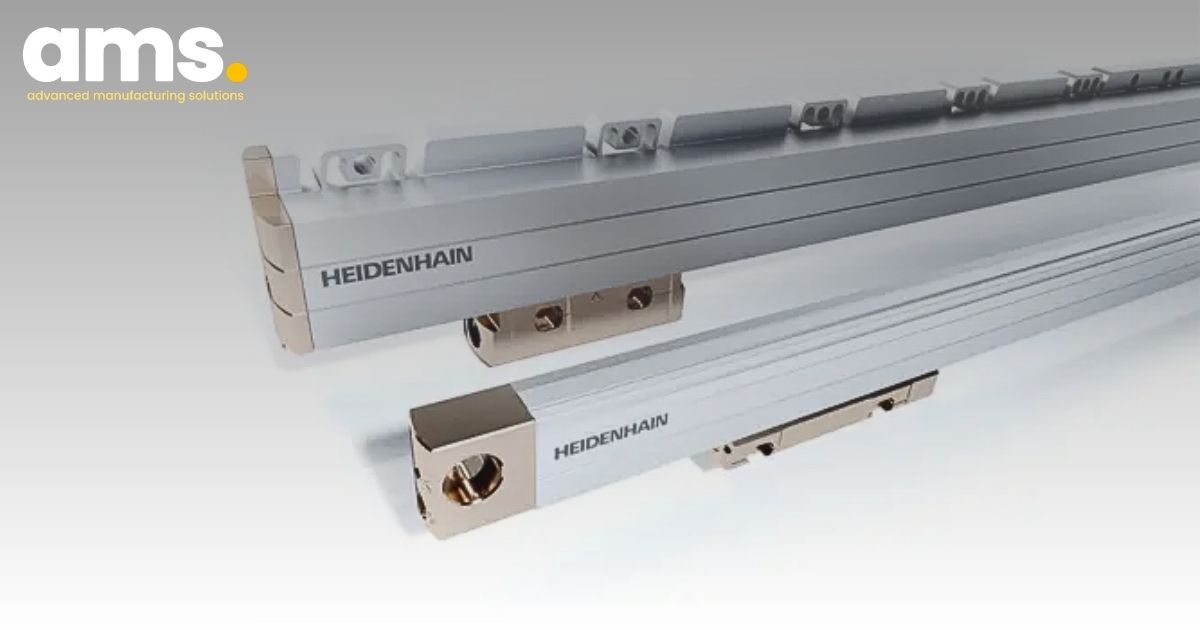
To access all machining positions on extremely large or elongated components, such as an aircraft fuselage or when producing large composite fiber components, robots can be moved along the length of the component on linear axes. HEIDENHAIN offers enclosed linear encoders of up to 30 m in length for accurately positioning robots with a linear drive. The position measurement from a linear encoder compensates for thermal errors and other factors affecting the feed mechanisms, which are not accounted for by traditional position detection methods based on the pitch of the recirculating ball screw and the angular position of the rotary encoder on the motor.

2. Summary: Enhanced precision in position measurement leads to improved accuracy at the tool center point
By employing secondary encoders on all of a robot’s axes and using linear encoders to position the robot in relation to the workpiece, industrial robots with the proper equipment can achieve the level of accuracy at the tool center point needed to execute precise machining and handling tasks on components. Angle and linear encoders from HEIDENHAIN and AMO not only deliver the essential system accuracy but also offer the required installation flexibility for complex and compact robot mechanisms. The compatibility of these encoders for safety-related applications also enables the implementation of human-robot collaboration systems.
Need help choosing an encoder for an automation project? Contact us now.
|
Comparison of the Most Important Specifications for Typical Secondary Encoders |
|||
| ECA 4000 | ECI 4000 | WMR | |
| Scanning principle | Absolute, Optical | Absolute, Inductive | Incremental, inductive |
| Inside diameter | 70 mm to 512 mm | 90 mm / 180 mm | 60 mm to 10 000 mm |
| Resolution | 29 bits | 20 bits | Depends on the subsequent electronics |
| System accuracy | ±2“ | ±25“ / ±40“ | ±3“ per meter of arc length |
| Resistance to contamination | + | ++ | ++ |
| Mounting tolerances | + | ++ | + |
3. HEIDENHAIN: Leading the Way in Precision Solutions
HEIDENHAIN stands at the forefront of precision solutions, offering cutting-edge technology and expertise in the field. With a rich history of providing high-precision measurement and control equipment, HEIDENHAIN has continually set industry standards and earned a reputation for unmatched quality and reliability.
Founded in 1889, HEIDENHAIN has been a key player in driving innovation and excellence in precision measurement and motion control. Their portfolio includes state-of-the-art angular and linear encoders, digital readouts, and numerical controls, all designed to deliver uncompromising accuracy and efficiency in various industrial applications.

In Vietnam, AMS Company Limited proudly serves as the authorized distributor of HEIDENHAIN products. As a trusted partner, AMS offers access to a comprehensive range of HEIDENHAIN solutions, ensuring customers in Vietnam have convenient and reliable access to the best products and services. For the most competitive pricings and unparalleled support, contacting AMS today is the first step toward leveraging HEIDENHAIN's exceptional precision solutions.
AMS Company, Ltd.243/9/10D To Hien Thanh, Ward 13, District 10
Hot line: 028.3868 3738/3903 - Fax: 028.3868 3797

